
Kaylee
DNA Reiplication
DNA replication is the basis for biological inheritance which is a fundamental process that occurs in all living organisms which copies their DNA for each cell and in order to produce offspring.
In the process of DNA Replication each strand of their original double strand DNAservesas a template for the new complimentary strand
DBA replication takes place in the cell cycle - sphase this takes place in the nucleus. DNA replication semi- conservative
Leading strand: 5' to 3' continuous copying moving toward helicase.
Lagging strand: 3' to 5' this copies in small sections called Okazaki fragment move away from helicase.
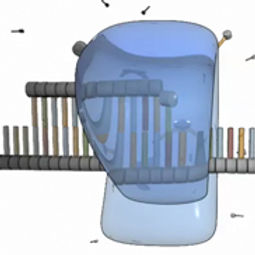
DNA replication is a crucial process; therefore, to ensure that mistakes, or mutations, are not introduced, the cell proofreads the newly synthesized DNA. Once the DNA in a cell is replicated, the cell can divide into two cells, each of which has an identical copy of the original DNA.

DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell.
The replication process relies on the fact that each strand of DNA can serve as a template for duplication. DNA replication initiates at specific points, called origins, where the DNA double helix is unwound. A short segment of RNA, called a primer, is then synthesized and acts as a starting point for new DNA synthesis. An enzyme called DNA polymerase next begins replicating the DNA by matching bases to the original strand. Once synthesis is complete, the RNA primers are replaced with DNA, and any gaps between newly synthesized DNA segments are sealed together with enzymes.
